RFID Flows
Handling RFID cards is completely optional, and if preferred the Payter terminal can be configured to treat all non-EMV cards as "Not accepted". Cardholders who present these cards, in this configuration, will see this message and the terminal will resume reading for an EMV card.
RFID Use Cases
There are a few main reasons to use RFID cards, but the below is not an exhaustive list:
- The card is an E Mobility Service Provider card and can provide free EV when authenticated or authorized
- The card is part of a closed user group e.g. a staff card, that provides goods from a vending machine inside a corporate HQ
- The card identifies the user in some other way e.g. a card that allows customized access to the Controller interface
An RFID card is a type of smart card that uses Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to wirelessly communicate data between a card and a reader. The card contains a small chip and an embedded antenna, which enable it to transmit information via radio waves when it is brought close to an RFID reader—no physical contact is required.
Contactless cards use RFID, but so do hotel room door keys, vehicle remote keys, and Google & Apple Pay.
Not all RFID cards can be read by Payter terminals, but most cards used for secure purposes can.
RFID Flows
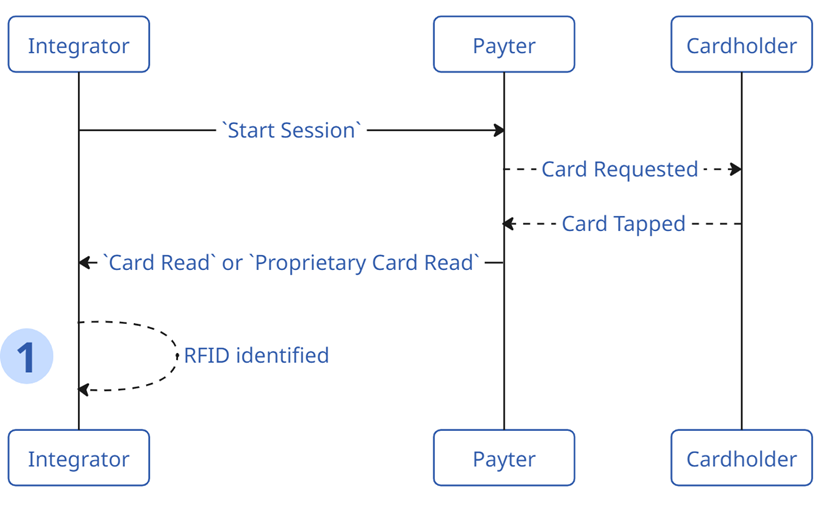
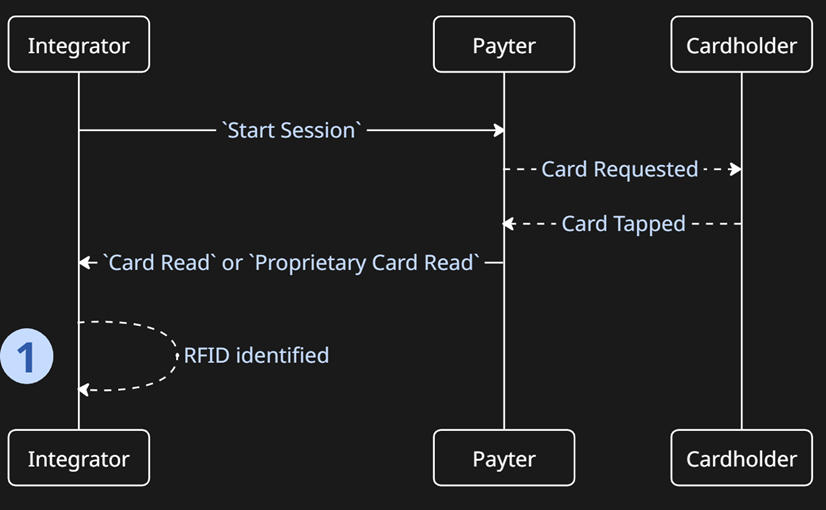
Scenario 1 - Card Read Only
In the below flow, the Payter terminal is simply used to read the card data and return it to the Integration Controller for them to complete the next steps. PSP has no role to play following the return of the Card Data.
Comments
- The only action needed here is to interpret the data that is returned, and action according to the Controllers needs. PSP can have a
Cancel Sessionsent to return it to anEnabledstate, ready for the nextStart Session.
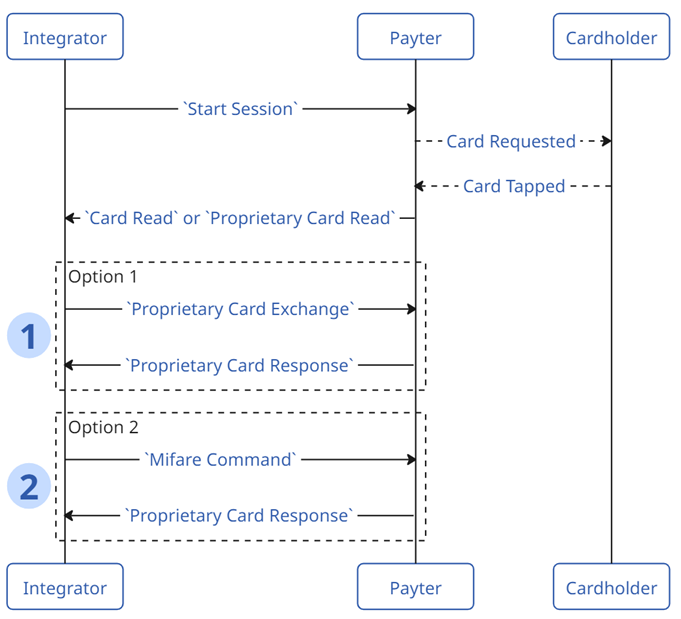
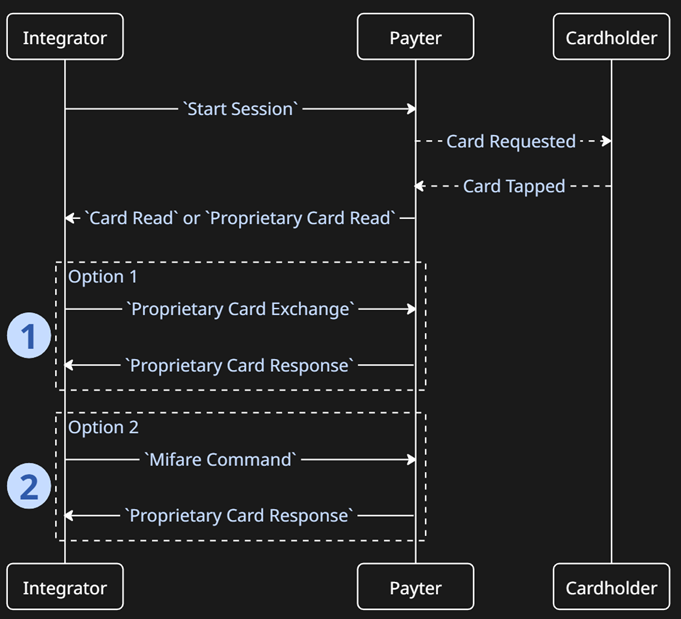
Secnerio 2 - Card Read/Write
This flow is only available on the APOLLO terminal family.
Comments
Proprietary Card Exchangeis used to send data to the card e.g. a Command Application Protocol Data Unit (CAPDU).Mifare Commandis used to read or write data to a Mifare card.
This functionality is advanced and determined by the RFID card technology being used. Working with RFID cards is optional. Writing Data or sending Commands to these types of card is rarely required.